Built-in LESS parser
The Quark template fully uses LESS language for generating the CSS files of the template. Thanks to the built-in LESS parser you can forget about additional LESS compilers - if you enable the template built in compiler then after every change in the template less files you will get new css files.
The LESS language features are described in the official documentation page.
Please remember that if you decide to modify the *.css files you shouldn't enable the LESS parser - after enabling it you will lose your CSS changes - it will be overwriten by the code based on the not modified *.less files.
The LESS compiler can be enabled under the template advanced settings:
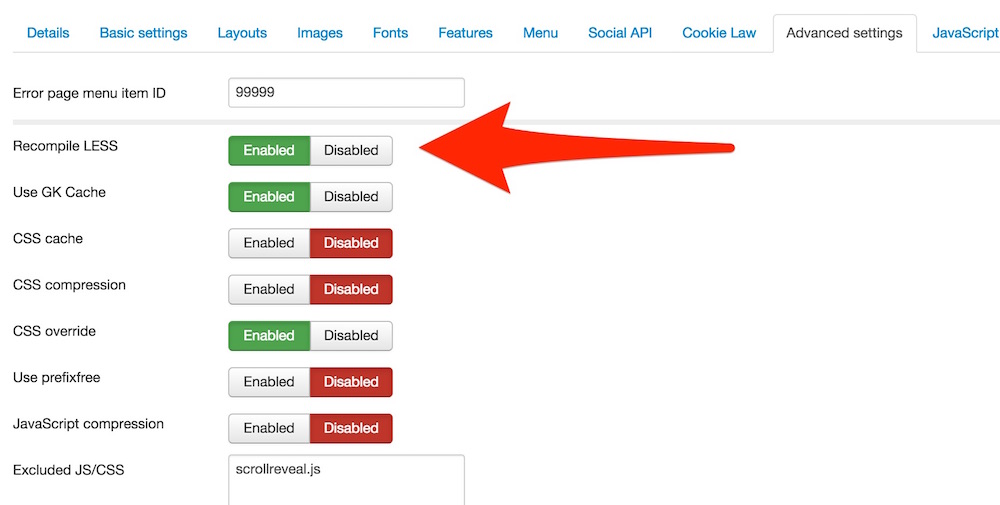
Please remember that the LESS parser should be enabled only while you are editing your LESS files - it needs relatively big amount of server resources and will cause slower page loading time. That's why please remember to disable the LESS compiler after finishing the *.less files modifications.
The LESS files are located under the less directory. Most of the files are loaded inside the main.less file which transform into the template.css file. Thanks to that we have limited amount of the CSS files request while you still have separate files like template.less, gk.stuff.less, k2.less etc.
The most important feature is fact that you can change easily the template colors and font-sizes using one file - variables.less. This file contains a variables with basic colors and font-sizes used inside the template CSS code. By changing one variable i.e. @primary_color, you can change the whole template colors.

 +34 623 977 856
+34 623 977 856 Calle Armando Cotarelo 16, Vegadeo, Asturias
Calle Armando Cotarelo 16, Vegadeo, Asturias